Exploring the Future of Web 3.0: A Deep Dive into Decentralization
Written on
Understanding Web 3.0
Web 3.0, often dubbed the decentralized internet, represents the third iteration of online connectivity. Currently, we are navigating through Web 2.0, where users trade their personal data for services. Unfortunately, this means that users relinquish ownership of their data once it is shared for personalized experiences.
This data is then utilized by advertising firms to curate targeted advertisements that align with users' interests and engagement patterns. While this practice isn't illegal, as users consent to the use of their data for personalized ads, it raises ethical questions regarding data ownership and privacy. In 2021, platforms like Google, YouTube, and Facebook attracted over 100 billion views, highlighting the dominance of major websites in our digital landscape.
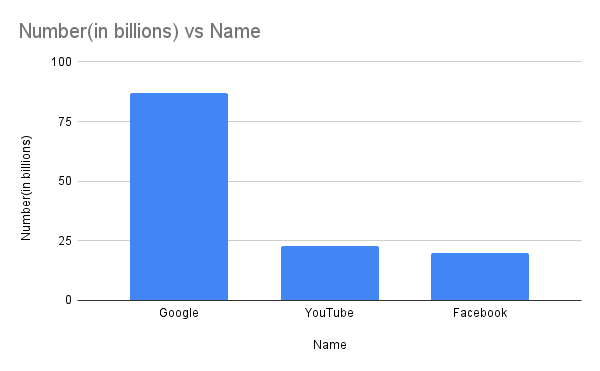
According to a chart from Statista, these leading websites are largely unchallenged. However, governing agencies hold the power to block access to specific websites or applications in certain regions, restricting users’ online experiences. The control extends to payment transactions, where users may find themselves unable to complete purchases due to arbitrary restrictions.
What Lies Ahead?
The advent of Web 3.0 promises a radically different future for the internet, characterized by decentralization. In this version, no single entity can dominate or restrict access, ensuring that anyone with an internet connection can engage freely and conduct transactions without the need for central authority approval.
Imagine a scenario where you never encounter the message, "This service is blocked in your area"—that's the essence of Web 3.0. Its decentralized structure means there are no regional barriers; services are open to all. This third generation of the internet prioritizes interactivity and user empowerment, eliminating centralized governance.
Web 3.0 operates on blockchain technology, which guarantees that data remains immutable.
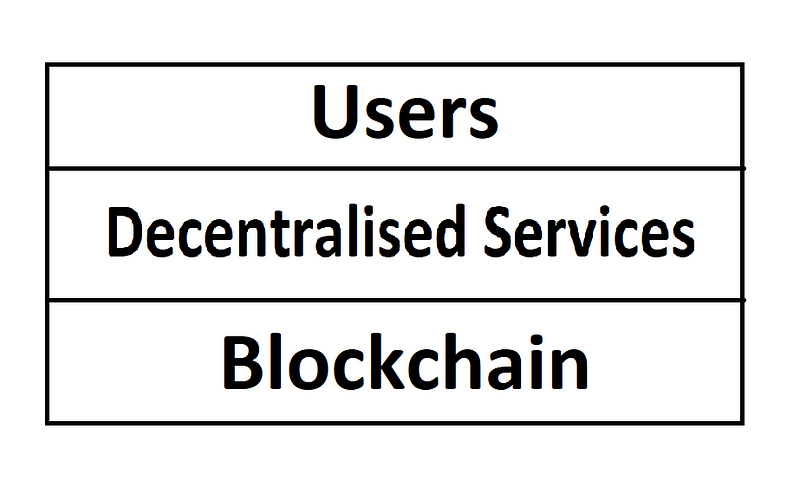
Blockchain technology functions by storing data in blocks spread across a vast network, making it nearly impossible to alter or manipulate information. Each block is identified by a unique hash, and any change to the data results in a modified hash, effectively invalidating that version of the blockchain. With multiple copies across diverse networks, tampering with one won't compromise the integrity of the system.
Further Insights on Web 3.0
In the realm of Web 3.0, websites and applications operate across various systems, ensuring independence from any single cloud platform. Backed by robust blockchain technology, Web 3.0 stands as a formidable advancement in internet capabilities. Its decentralized network comprises peer-to-peer nodes, enabling secure payment transactions that do not require personal information. This transparency fosters reliability, as there is no single entity governing the system.
The enhanced computing power and decentralized nature of Web 3.0 significantly reduce the likelihood of system failures or outages. Payment systems are evolving from traditional centralized methods to decentralized alternatives, such as Ethereum, Bitcoin, and USDT (Tether), which maintains a stable value around $1.
While Web 3.0 holds immense promise for security and reliability, it remains in the early stages of development, and widespread adoption is still a work in progress. A major hurdle to its acceptance is a general lack of awareness among potential users.
Transitioning from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0 is expected to be gradual, with no clear timeline for when this shift will occur on a large scale. Ultimately, Web 3.0 aims to empower users, allowing them to shape their internet experiences freely.
This article is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial or legal advice.
The first video titled "Web 3.0 Design: The Future or Another Internet Fad?" discusses the potential implications and challenges of Web 3.0 in the context of design and user experience.
The second video, "What's Web3 | How Does Web 3.0 Work," provides a comprehensive overview of the mechanisms behind Web 3.0, emphasizing its operational principles and foundational technologies.
If you found this exploration valuable, consider subscribing for more insights on technology and innovation.