Innovative Energy Storage: Transforming Bricks into Power Sources
Written on
Chapter 1: Renewable Energy Storage Solutions
In recent years, the ability to store energy produced from renewable sources at industrial locations has gained traction. Surprisingly, bricks have emerged as an effective medium for this purpose.

As you may know from following climate-related news, renewable energy has become more affordable than fossil fuels in certain areas. However, the challenge of intermittency—where energy production doesn't always align with consumption—remains significant. The sun doesn't shine constantly, nor does the wind blow consistently, but energy demand continues unabated. This calls for innovative storage solutions, and the answer may lie within the humble brick.
Superheated Brick Batteries
To illustrate the wastage associated with renewable energy, consider that in Great Britain, 5.8 TWh of wind power was curtailed during 2020 and 2021 due to system limitations—sufficient energy to supply 800,000 homes. When renewable energy is unavailable, fossil-fuel power plants must be activated, leading to both energy loss and increased carbon emissions.
Efforts to tackle this issue are underway, particularly by startups like Rondo Energy, which recently secured significant investments from the European Union and Bill Gates. Their goal is to decarbonize industrial processes using innovative superheated brick batteries. According to Rondo’s CEO, Eric Trusiewicz, this technology aims to eliminate the "green premium" associated with electrifying industrial heat, offering scalable solutions.
Rondo's approach involves utilizing zero-carbon renewable energy to power heating elements, akin to those found in household appliances. These elements generate heat, which is then used to warm substantial quantities of bricks, effectively storing thermal energy.
When heat is required, air circulates through the heated bricks, reaching temperatures exceeding 1000°C. This superheated air, or steam when water is added, can then be utilized for various industrial applications.
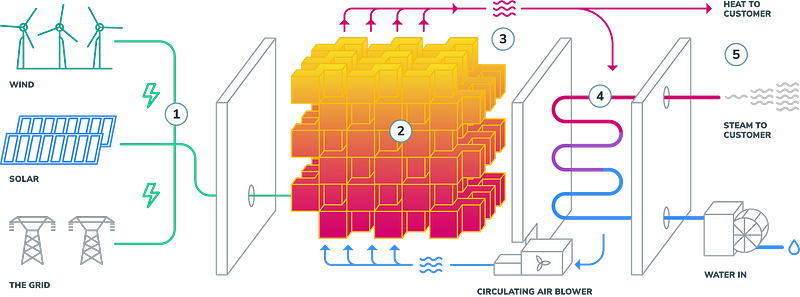
Rondo’s technology is a specific example of a broader system known as thermal energy storage (TES), which also includes alternatives like salt, air, and water. TES systems maintain thermal energy without needing conversion, enhancing energy efficiency. Furthermore, the materials employed are commonly available and environmentally friendly, allowing for large-scale deployment without depleting resources. The bricks used in Rondo’s system also promise virtually unlimited cycles, as they do not degrade over time.
Energy Storage via Gravity
An additional effective method for storing energy involves converting electrical energy into potential energy through gravity. One well-known example is pumped hydropower storage, a straightforward concept often covered in physics courses. Water is pumped to an elevated reservoir during periods of low demand and released to generate electricity when needed.
Interestingly, bricks can also facilitate a similar mechanism. In Rudong, China, large bricks weighing 24 tons are lifted more than 300 feet by an elevator powered by renewable energy. Managed by Energy Vault, this facility employs a trolley system to transport bricks during times of low electricity costs. When energy demand arises, these bricks can be released, generating power as they descend.

Brick Batteries: A Promising Concept
Bricks can also serve as supercapacitors. Research published in Nature Communications reveals that standard red bricks can be coated with a novel nanofibrillar polymer known as PEDOT. The iron oxide, which gives bricks their characteristic red color, acts as an excellent substrate for this coating, transforming the bricks into electrochemical electrodes capable of storing charge.
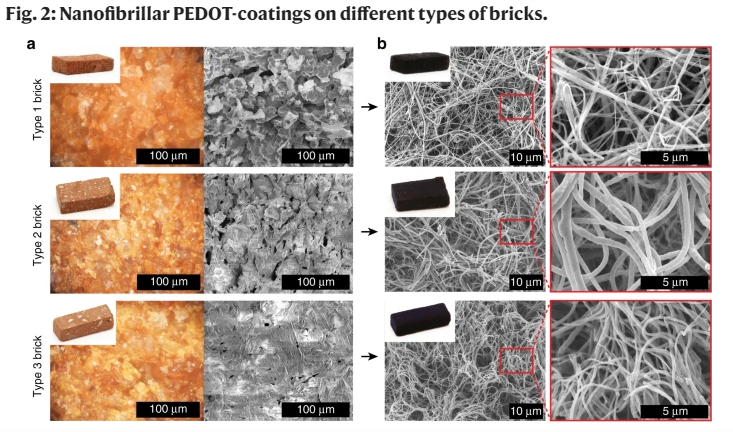
While these bricks can store energy quickly, their energy density is only about 1% that of lithium-ion batteries. However, supercapacitors can undergo many more charge and discharge cycles than traditional batteries, which deplete as their chemical components are consumed. Despite seeming limited in capacity, initial prototypes have demonstrated enough power to operate small LED lamps, and stacking multiple bricks can enhance energy storage potential for more demanding applications.
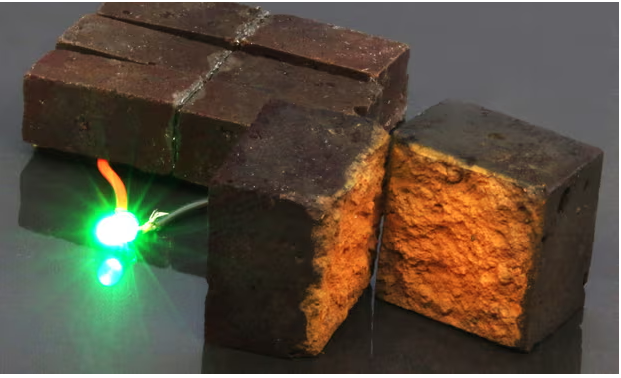
Though brick batteries are still in the experimental phase, they are garnering significant research interest aimed at improving performance. These innovations could potentially reduce the reliance on lithium and other scarce metals in renewable technologies. Furthermore, brick batteries could complement home solar systems, enabling them to power small devices.
The best solutions often come from the simplest ideas. Bricks, one of humanity's oldest and most utilized building materials, may hold the key to innovative energy storage. Transforming this readily available resource into a sustainable energy solution might sound like science fiction, but with dedicated effort, it could soon become a reality. As Mukesh Ambani wisely stated, "The solution to pollution is not dilution. It’s innovation."
For additional insights on sustainability and environmental topics, please visit my blog. If you appreciate this content and wish to support my work, feel free to buy me a coffee!
Chapter 2: Video Insights on Energy Storage
In this section, we explore two informative videos that delve into the role of bricks in energy storage solutions.
The first video discusses how energy-storing concrete bricks could play a crucial role in the expansion of renewable energy technologies.
The second video highlights how a brick and rock battery is revolutionizing energy storage systems.